Technology research report for antibiotic & antimicrobial resistance discusses therapeutics challenges, innovations, & new technical approaches. The report also covers startups, companies, global trends, collaborations & acquisitions.
Antibiotic resistance determinants are the genetic factors that are possessed by some bacteria which are responsible for resistance to certain antibiotics and chemical antibacterial agents. Most often these antibacterial agents are sulfa drugs. It is well-established fact in microbiology that antibiotic resistance determinants are transferable from donor bacteria to recipient bacteria. In this report, we will talk about the alternative therapies that aid in combating antibiotic- resistance. It is believed that this transfer of resistance determinants is mediated via RTF factors.
Report on Antimicrobial & Antibiotic Resistance and Therapeutics
The objective of the study is to explore the emerging, novel, and innovative trends in the field of “Antimicrobial Resistance & Therapeutics”. The study will include various therapies that have been developed to combat Antimicrobial Resistance. The commercialization aspects such as Products, Existing companies, Startups are also discussed.
Report on Alternative therapies to tackle antibiotic & antimicrobial resistance
The technology research report for therapeutics will shed light on the advancing and innovative technologies that are shaping up the industry.
Phage Therapy
Recombinant phages are developed to deliver antimicrobial proteins in target bacteria.
Probiotics
Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium have been used for the treatment of various gastrointestinal infections, the potency of the yeast Saccharomyces boulardii, and of nonpathogenic strains of E. coli and Bacillus spp., has also been explored.
Antimicrobial peptides
These peptides are facially amphiphilic and their cationic domain engages in electrostatic interactions with the negatively charged bacterial cell surface, while the hydrophobic domain interacts with the lipids of the bacterial membrane.
Antibodies
Antibodies could be used to treat bacterial infections either by directly targeting the bacterial surface or indirectly by neutralizing the bacterial toxins and the virulence factors that are responsible for the infection.
Nanoantibiotics
Metal and metal oxide-based nanoparticles and antibiotics can either be used to deliver antimicrobial substances or may contain antimicrobial substances.
Fecal Microbiota transplant
This technology includes the introduction of the microbiome from a healthy donor to a diseased gut.
CRISPR/ Cas9
Temperate phages were used to deliver the CRISPR-Cas system into the genome of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Lysins
Lysins can be engineered to kill several pathogens including Gram-negative bacteria. These enzymes have attractive features that they do not activate an adverse immune response and a raise of resistance is very unlikely.
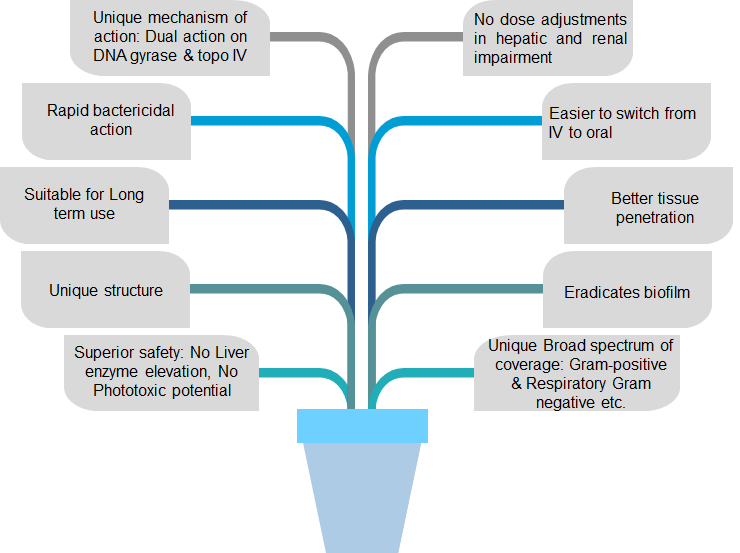
Gepotidacin
- Description: Gepotidacin is a first-in-class, triazaacenaphthylene antibiotic with the unique ability to selectively inhibit bacterial DNA replication by a means not utilized by any currently approved human therapeutic agent.
- It is used to treat Urinary Tract Infections in human caused by various microbial strains for treating infections caused by Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
- It is effective against few ESKAPE pathogens such as Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterobacter spp. which is highly virulent strains
- This new antibiotic compounds exhibit more potent antimicrobial activity with novel mechanisms of action.
Mode of action
- It has “dual targeting” mechanism of action (MOA) and oral formulation. Its MOA is distinct from any currently approved antibiotic.
- It works by selectively interacting with two key bacterial enzymes, DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV (type II topoisomerases), responsible for bacterial replication. The novel MOA confers activity against most target pathogens resistant to established antibiotics, including fluoroquinolones.
- The development of gepotidacin is the result of a successful public-private partnership between GSK, the US government’s Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA) and Defense Threat Reduction Agency (DTRA). This collaboration was established in 2013 with the aim to support the development of several antibiotics to fight antibiotic resistance and bioterrorism.
About the EAGLE (Efficacy of Antibacterial Gepotidacin Evaluated) phase III programme
The phase III clinical program for gepotidacin in adults and adolescents comprises the following two studies:
Urogenital gonorrhoea study: The EAGLE-1 study will compare the efficacy and safety of gepotidacin (3000mg administered orally at the study site followed by self-administration of a second oral 3000mg dose as an outpatient 6 to 12 hours after the first dose) to a single intramuscular 500mg dose of ceftriaxone plus a single oral 1g dose of azithromycin in approximately 600 patients with uncomplicated GC caused by the bacterium NG. The study duration is approximately 21 days. The primary endpoint will be the culture-confirmed bacterial eradication of NG from the urogenital body site at the Test-of-Cure (TOC) visit.
Uncomplicated urinary tract infection study : The EAGLE-2 study will compare the efficacy and safety of gepotidacin (1500mg administered orally twice daily for 5 days) to nitrofurantoin (100mg administered orally twice daily for 5 days) in approximately 1,200 adolescent and adult female patients with uUTI. The study duration is approximately 28 days. The primary endpoint will be the therapeutic response at the TOC visit in patients with qualifying uropathogens.
Each year Signicent provides consultancy to hundreds of organizations to help transform their innovations to value.
EMROK by Wockhardt
Description:
- EMROK (IV) and EMROK O (Oral) has been approved by Indian drug regulator DCGI.
- It is effective for acute bacterial skin and skin structure Infections including diabetic foot infections and concurrent bacteremia.
- It is effective against superbug like Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
Novel Temporin-L antimicrobial peptides to tackle Superbugs
The Antimicrobial Peptides (AMP’s) is one of the promising therapies but it leads to cellular toxicity and is usually specific towards a single type of microbe.
The AMP’s with the broad antimicrobial spectrum should be synthesized which can be done by making the modification the basic structure of the peptides and reducing the cellular toxicity.
Report on R&D Group working in the area of antibiotic & antimicrobial resistance
University of Naples Federico II, University of Rome (Italy), 2020University of Naples Federico II, University of Rome (Italy), 2020
Technology
Inducing self-assembling properties in cationic peptides and influence their interaction with bacterial membranes and consequently their antimicrobial and broad-spectrum activity.
Temporins
- One of the riches source of AMPs is the amphibian skin of the Rana genus.
- Temporins, isolated from the skin secretions of the European red frog Rana Temporaria, is isoforms of AMPs.
- The isoform L (temporin L, TL), is a highly potent AMP with activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
Mode of Action
- Phenylalanine zipper motif, are involved in the initial peptide binding to the Gram-positive cytoplasmic membrane and the stabilisation of peptide aggregates inside the membrane, leading to the formation of large pores and consequential cell death.
- For gram-negative bacteria, the mechanism of permeabilisation appears to be different instead and may not involve membranolytic processes.